What Best Describes the Citric Acid Cycle
This produces ATP by pumping protons through chemiosmosis. The first reaction of the citric acid cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme citrate synthase.
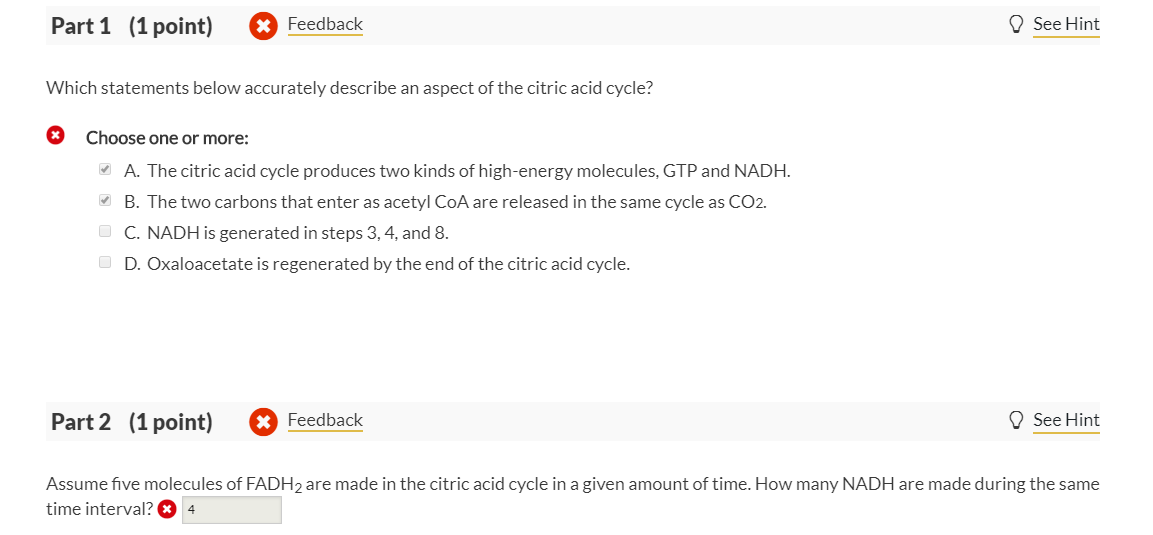
Solved Part 1 1 Point Feedback See Hint Which Statements Chegg Com
The citric acid cycle also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle is a series of chemical reactions in the cell that breaks down food molecules into carbon dioxide water and energy.

. Krebs citric acid cycle. Biology questions and answers. D Glycolysis produces pyruvate which directly enters the citric acid cycle.
1-The oxidation reactions of the citric acid cycle provides oxygen for electron transport and ATP synthesis. Researchers suspect that portions of the reverse cycle may have been responsible for fixing CO2. Which of the below best describes the citric acid cycle.
It catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres compensating for the shortening that could occur during replication. Which statement best describes how the citric acid cycle relates to glycolysis oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis. This process joins 2 pyruvic acid molecules into a molecule of glucose.
In prokaryotes these steps both take place in the cytoplasm. Through a series of steps citrate is oxidized releasing two carbon dioxide molecules for each acetyl group fed into the cycle. Regulation of oxidative phosphorylation.
The ATP produced is utilized in large amount in the process of glycolysis. 3-In the citric acid cycle oxaloacetate is regenerated which is available to pick up acetyl CoA and start the cycle again. The TCA cycle also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondria and provides large amounts of energy in aerobic conditions by donating electrons to three NADH and one FADH flavin adenine dinucleotide which donate electrons to the electron transport chain creating the proton gradient.
The citric acid cycle also known as the Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle is at the center of cellular metabolism playing a starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. Breakdown of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate d. The citric acid cycle.
Regulation of Krebs-TCA cycle. The major energy provider of the cell. The last part of.
This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the ATPs in cellular respiration. This cycle produces NADH and FADH2 which donate electrons to the electron transport chain to pump protons and produce ATP through chemiosmosisProduction of ATP using an electron transport chain and chemiosmosis is called oxidative phosphorylation. This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 ATPs for each glucose.
Many bacteria perform the. O A The citric acid produces pyruvate which converts to glucose to enter glycolysis. It loses a hydrogen atom and loses potential energy.
The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced which generate ATP in the electron transport chain. This cycle produces NADH and FADH _2 which donate electrons to the electron transport chain to pump protons and produce. Transfer of energy via electrons in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions to make ATP c.
This cycle produces NADH and FADH _2 which donate electrons to the electron transport chain to pump protons and produce. It finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. Which of the following best describes how the citric acid cycle relates to glycolysis oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis.
2-The reduction reactions of the citric acid cycle produce ATP molecules. Only in the citric acid cycle. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase.
This cycle produces the energy currency that undergoes the electron transport chain to produce water and ATP. Citric Acid cycle also known as Krebs cycle or Tricarboxylic acid cycle is the second stage of the cellular respiration unique to aerobic organisms. In both gylcolysis and citric acid cycle D.
Researchers suspect that early methods for converting pyruvate to. Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs who postulated the detailed cycle. Which of the following best describes how the citric acid cycle relates to glycolysis oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis.
Glycolysis produces pyruvate which is converted to acetyl-CoA and enters the citric acid cycle. The citric acid cycle is a closed loop. In the citric acid cycle the acetyl group from acetyl CoA is attached to a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon citrate molecule.
Citric acid cycle occurs in the intracellular space or matrix of the mitochondria of eukaryotes. In eukaryotes the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria just like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl. The citric acid cycle oxidizes glucose to carbon dioxide.
Which statement describes the citric acid cycle. Mitochondria apoptosis and oxidative stress. The citric acid cycle also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle is the second stage of cellular respirationThis cycle is catalyzed by several enzymes and is named in honor of the British scientist Hans Krebs who identified the series of steps involved in the citric acid cycle.
It allows recovery of energy from carbohydrates only. Glycolysis produces pyruvate which is converted to acetyl-CoA and enters the citric acid cycle. Researchers suspect that the original citric acid cycle was used by all species.
Oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis. In plants and animals eukaryotes these reactions take place in the matrix of the mitochondria of the cell as part of cellular respiration. Glycolysis produces pyruvate which is converted to acetyl-CoA and enters the citric acid cycle.
3 The citric acid cycle depends on the availability of NAD which is a product of glycolysis. Once the two molecules are joined a water molecule attacks the acetyl leading to the release of coenzyme A from the complex. 2 The citric acid cycle produces most of the ATP that is subsequently used by the electron transport chain.
The formation of glucose de-novo from other molecules O b. In this step oxaloacetate is joined with acetyl-CoA to form citric acid. Which answer best describes the role of telomerase in replicating the ends of liner chromosomes.
View the full answer. This pathway produces NADH and FADH2 which enter through chemiosmosis. Which statement describes the citric acid cycle.
Which of the following best describes the importance of the citric acid cycle as a central pathway of metabolism.

Solved 4 Which Of The Following Best Describes The Chegg Com

Solved 5 Which Of The Following Best Describes How The Chegg Com

Solved Which Statement Describes The Citric Acid Cycle This Chegg Com
No comments for "What Best Describes the Citric Acid Cycle"
Post a Comment